Activation Function
The function applied at neurons of a neural network to get output for provided input values is Activation Function. We can see the function in given figure:
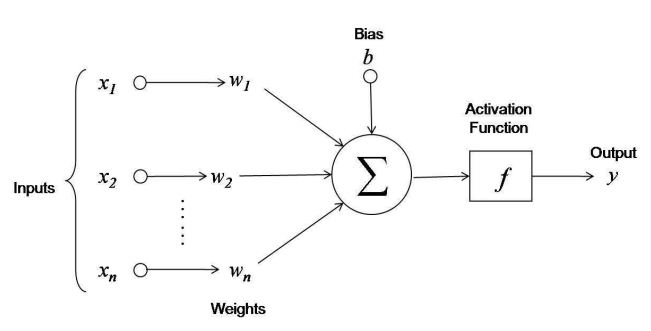
Here we can see the summation of outputs of network is passed through activation function. So, the output of the network y looks like:
So, why do we need activation function then ?
The activation fucntion is introduced in the network due to following reasons:
- To introduce non-linearitites in the neural network. If we pass layers of neural network through linear functions only then the output provided will also be linear output. It might be able to learn some simple data but will not be able to comprise the complexities of many machine learning datas which have many features as input. It might also not generate the weight values required for generalized dataset.
- It simply determines whether the neuron most be activated or not. It acts as threshold to the neuron. It is used to predict the information on the basis of relevance of provided input. Let us, take example of sigmoid activation function in which is represnted by formula: Here, the value of function ranges from 0 to 1 when e^x is 0 or infinity respectively. Thus, neurons are activated when the value of activation function is greater than zero and is not when the value approaches zero. Thus the function acts as threshold.
- It limits the value to be learned in required range. Otherwise output of neural network might range from -inf to inf. Thus, producing no relevant results.
There are many variations of activation fucntion. But, three of them are used extensively. They are:
-
Sigmoid Activation function:
Sigmoid activation function is denoted by : which also can be written as:
The value of this function ranges from 0 to 1 and it can be represented in the figure as:
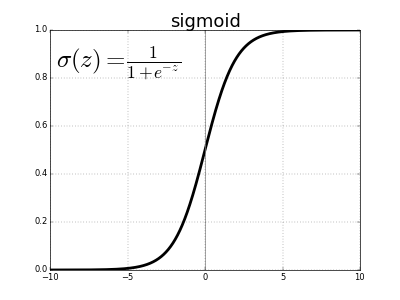
The sigmoid activation function is usually used for binary classification problem where output is predicted as false(0) if the value is less than 0.5 else predicted true(1).
-
Tanh Activation function:
Tanh activation function can be represented as: $$ f(x) = (e^x - e^-x)/(e^x + e^-x)
It’s value ranges from -1 to 1 and can be illustrated as:
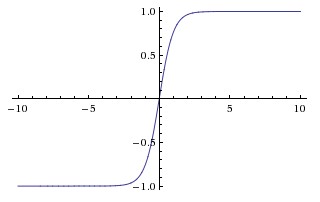
Tanh activation function is used in the scenarios where output is not sufficiently covered by Sigmoid activation function. It can be used for activation function in larger range and can also be used to predict classes at different labels like tends to -1 for one class, approximate to zero for another class and approximate to 1 for other.
-
ReLU Activation function: ReLU(Rectified Linear Unit) is denoted as: and
It is represented by following figure:
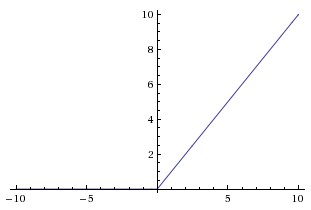
This function is introducted recently than other two function. This was introduced to overcome a major problem in above two function, which is vanishing gradient problem. For the graph of above two function we can see that the gradient of function approaches to zero when the values of function approaches to |1|. If this happens the optimizer funtion will no more be able to learn from the input values as gradient approaches zero. So, to overcome this problem ReLU was introduced whose value ramges from 0 to x. This also has one major problem which is dying ReLU problem. For this other variations of ReLU like Parameteric ReLU, Leaky ReLU are introduced where it has some small value for even zero input to the activation function.
How is ReLU non-linear activation function?
Relu is non linear activation function since it doesnot contain formula of straight line. It is actually piece-wise linear activation function where it is equal to zero if value of input is zero and x i.e. straight line for input greater than zero.

