Understanding ANN
We have a rule in our college that we cannot choose the topics or algorithms that our senior had done in previous year. Since, we were willing to do a project related to prediction of disease. Our seniors had done a project on pneumonia detection using Bayesian Network. So, we had no any algorithm of choice rather than Artificial Neural Network; that’s what we thought at that time.
Firstly, let’s start with Artificial Neural Network which we had researched at our very first month of project. Artificial Neural Networks is simply the structure used to calculate output based on input, hidden layer followed by activation functions to produce desired result.
Now let’s discuss about each aspect of neural network in brief: ANN consists neurons, weights, biases and layers.
- Neurons consists of values calculated using activation function and biases(We will discuss more about this in later post)
- Weights are the values between neurons from one layer to another.
- ANN consists minimum of three layers: input layer, hidden layer and output layer. If a network consists of only one hidden layer it is also referred as one layer network.
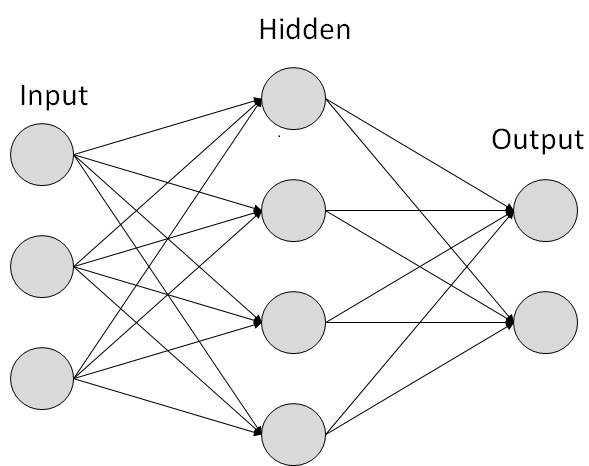
The first figure illustrates basic ANN which consists of a input layer, hidden layer and output layer. We can see that input layer consists of two neurons, hidden layer consists of four neurons and output layer consists of two neurons. The number of input neurons are the number of feature value we want to pass to a neural network so that it can produce desired result. The number of outputs are the expected number of classes or predictions we want as a result from our neural network and the number of neurons in hidden layer are added according to the need of network while optimizing it. We will discuss more about this in upcoming post.
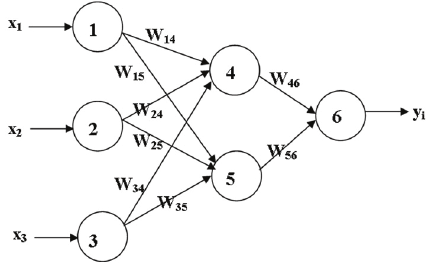
Figure 2 shows the distribution of weigths between layers in ANN. The weights are aligned from each neuron in previous layer to the neuron in next layer, i.e. For input-hidden layer, the weigths are aligned as: W14, W15, W24, W25, W34, W35. For programming this weights are expressed in matrix form. Thus, if either the number of layer increases or the values of neurons increses, the number of weight values will automatically increase. Hence, resulting in larger sized matrix.
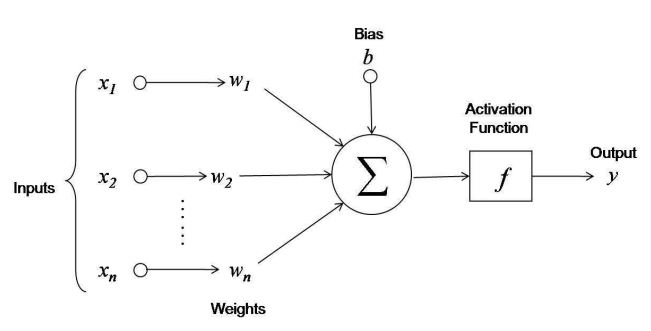
In figure 3 we can see neural network process in detail. Inputs are represented by x1, x2, … xn with weigths w1, w2, …wn and biases b. Biases are introduced in network as a constant which contributes to the weight value in next layer but are not affected by results of previous layer. This has many advantages like having a more parameter for neural network to generalize with, the network will even be abble to learn if all of the values from previous layer is zero. The simple representation of artificial network can be defined by formula,
For this figure the formula can be represented as,
Here, A is referred to an activation function of any kind like sigmoid, tahn and relu. This is applied to introduce non linearity in the network.
The features can be anything from array with image of animal to height, width of a tree. Similarly output can be classification like: cow, elephant, dog or prediction score that represnts a probabilty that an image is dog or not. Thich is also called regression.
The networks depicted in figures above is feed forward neural network. In this kind of network the weights are flowing from input layer->hidden layer->output layer. This is basic structure of Artificial Neural Network. Hence, in this post we became familiar with basic structure of Artificial Neural Network.
Figure References:
Figure 1.https://www.tutorialspoint.com/artificial_intelligence/images/atypical_ann.jpg
Figure 2.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Md_Rafiqul_Islam5/publication/221911789/figure/fig1/AS:304732305412105@1449665251675/An-example-of-a-multilayer-feed-forward-artificial-neural-network.png
Figure 3.https://i.stack.imgur.com/VqOpE.jpg

